Nigeria's adoption of the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards marks a watershed moment for African corporate transparency.
The Financial Reporting Council's pioneering roadmap leads the continent into a new era of climate, governance, and risk reporting excellence, opening doors for enhanced capital flows, trust, and competitiveness.
Nigeria Drives ESG Disclosure for Investment Growth
Nigeria is positioning itself as Africa's trailblazer in sustainability disclosure, stepping firmly onto the global ESG stage.
On June 26, 2023, the Financial Reporting Council (FRC) announced a forward-looking roadmap for implementing IFRS S1 and S2 standards, taking the country's largest companies from voluntary disclosure to mandatory reporting by 2028 and 2030.
This phased plan is crafted to accelerate investor confidence through clear, reliable sustainability and climate-related risk reporting.
For Nigerian corporates across sectors like banking, oil & gas, and manufacturing, this is a high-stakes opportunity to turn ESG compliance into a competitive advantage. The roadmap incorporates capacity-building, data assurance frameworks, and transition reliefs, easing the operational shift.
Partnerships with international financiers and advisory firms, including the World Bank, IFC, African Development Bank, and KPMG, reinforce the strategic ecosystem driving this transformation.
Tomi Adepoju, Partner and Head of Enterprise Risk and ESG Services at KPMG Nigeria, in their report "IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards: From Awareness to Implementation", underscores the report's focus: "We aim to highlight specifics of Nigeria's IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards Adoption Roadmap to move the conversation from awareness to implementation and value creation."
The rollout addresses key challenges, which include technical complexities, data gaps, and upfront costs, but firmly aims to embed ESG into boardroom strategy and investor engagement.
Early adopters set benchmarks for transparency and market readiness, unlocking new streams of ESG-driven capital. With disclosure becoming mainstream, Nigeria is steering a path to resilient growth and enhanced access to global markets.
Corporate Nigeria Enters a New Era of Sustainability Reporting
2023 and 2024 will be remembered as turning points for Nigeria's reporting ecosystem. In a first for Africa, the FRC's roadmap introduces not only world-class standards, but also systematic checks, such as readiness tests, phased assurance, and transition reliefs.
Early adopters gained public recognition, while a clock ticks down to the 2028 mandatory adoption deadline for Public Interest Entities (PIEs) and 2030 for SMEs. "Nigeria's bold move showcases its ambitions to tap global ESG opportunities," remarks Tomi Adepoju.
Roadmap Milestones (2023–2030)
Phase | Key Dates | Main Population | Requirements |
Early Adoption | Until Dec 2023 | Select entities | Readiness test, pilot reporting |
Voluntary Adoption | 2024–2027 | Voluntary PIEs/SMEs | Readiness test, phased reliefs |
Mandatory Adoption | From Jan 2028 | PIEs, then SMEs | Full standards, assurance |
Government/Orgs | TBD | Gov. entities | To be determined |

Adoption Roadmap, Standards & Operational Changes
Nigeria's IFRS journey unfolds in four phases, each requiring firms to pass the FRC's Readiness Test, evaluating governance, risk management, culture, and data capabilities.
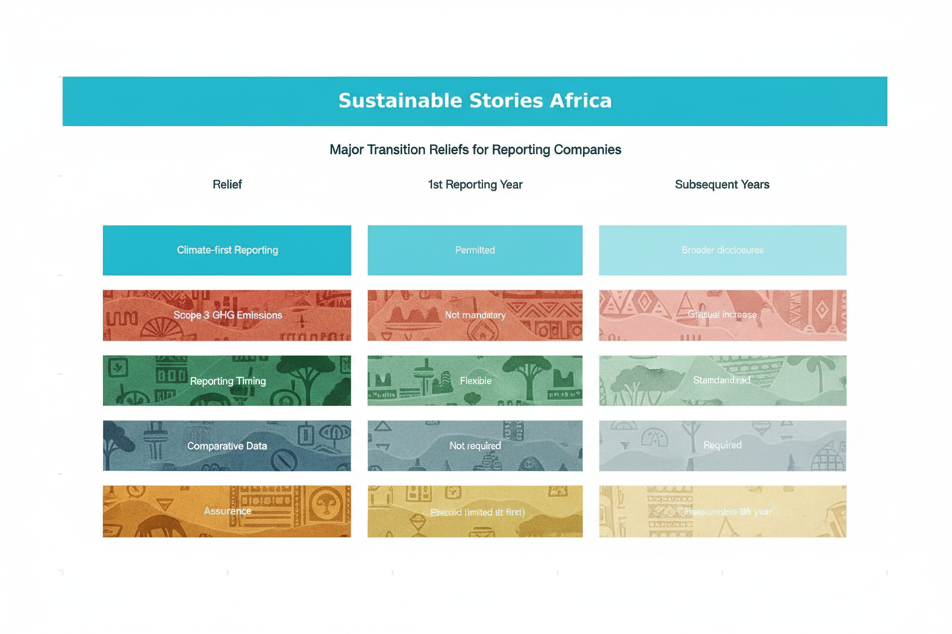
Transition reliefs feature climate-first reporting (initial focus on climate-related disclosures), scope 3 emission flexibility, comparative data exemptions, and phased GHG measurement methods.
Early capacity-building workshops, stakeholder engagements, and adoption guides support both preparers and regulators.
Major Transition Reliefs for Reporting Companies
Relief | 1st Reporting Year | Subsequent Years |
Climate-first Reporting | Permitted | Broader disclosures |
Scope 3 GHG Emissions | Not mandatory | Gradual increase |
Reporting Timing | Flexible | Standardized |
Comparative Data | Not required | Required |
Assurance | Phased (limited at first) | Reasonable by 5th year |
All entities must align reporting cycles with global standards, IFRS S1 and S2, TCFD, GRI, ESRS, tailored for local realities. Capacity-building support is a central theme, with the World Bank and UN SSE delivering joint training programs, and local champions like KPMG providing hands-on advisory.
Opportunity, Value Creation & Overcoming Barriers
With credible disclosure comes the promise of new capital flows, improved risk management, and reputational gains.
Nigerian corporates stand to attract ESG-focused investors while positioning themselves for international market access.
Yet adoption barriers persist, including cost, data quality, technical proficiency, and internal resistance. The FRC and ISSB have addressed these, offering adoption guides, knowledge hubs, and scalable platforms.
Key benefits:
- Enhanced transparency and trust with stakeholders
- Opportunity to unlock green/climate finance
- Improved risk management and strategic agility
- Elevated public reputation, helping firms compete regionally and globally

Key Enablers & Support Mechanisms
Support Mechanism | Key Partners | What’s Offered |
|---|---|---|
Capacity-building Workshops | FRC, ISSB, World Bank | Training, technical guides |
Adoption Guides | IFRS Foundation, ISSB | Roadmaps, standard advice |
Knowledge Hub | ISSB, KPMG | Data management/install kernels |
Beyond the Balance Sheet | IFC | Online tools, resources |
AfDB Collaboration | AfDB, ISSB | African context support |

Phased Implementation, Assurance & Data Management
Organizations now act on the roadmap—starting with gap assessments and board resolutions, moving through transitional and voluntary adoption phases, and culminating in mandatory reporting and comprehensive assurance. The timeline for assurance is phased: limited assurance in year three, expanding to reasonable assurance and inclusion of scope 3 emissions by year six. Firms must invest in technology, upgrade data systems, and develop tailored ESG strategies.

All entities must align reporting cycles with global standards, IFRS S1 and S2, TCFD, GRI, ESRS, tailored for local realities. Capacity-building support is a central theme, with the World Bank and UN SSE delivering joint training programs, and local champions like KPMG providing hands-on advisory.
Path Forward – Scaling Impact, Building Trust
Nigeria's leaders promise sustained capacity-building and regulatory alignment through 2030, with the FRC monitoring, advising, and evolving standards as realities change. As assurance frameworks cement trust, Nigeria's capital markets are poised for a surge and global relevance.
Summary Table: IFRS Adoption Benefits & Priorities
Priority | Promise | Key Actions |
Transparency | Global standard | Roadmap, readiness |
Capital Access | New investments | Phased, supported |
Climate Action | Reliable disclosure | Training, tech |
Trust | Stakeholder confidence | Assurance |














